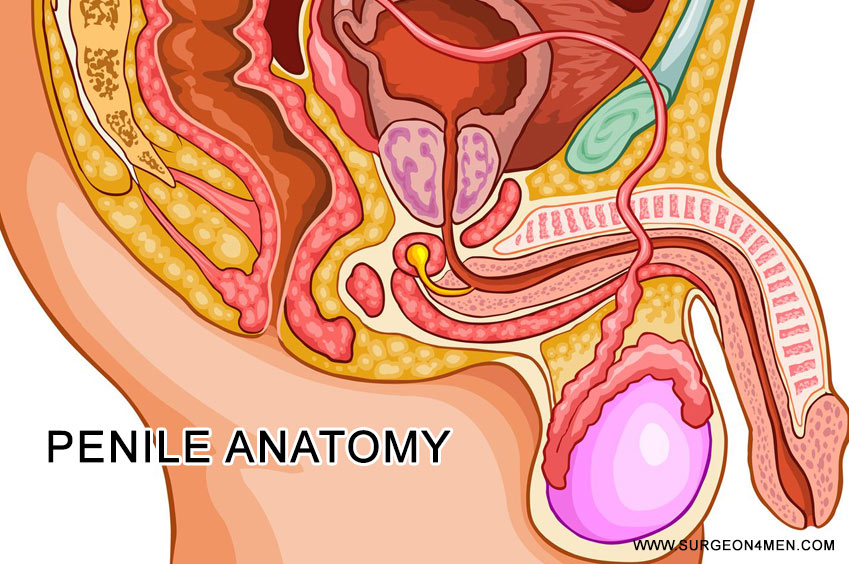
Penile Anatomy
The male penis is considered a dynamic external excretory as well as reproductive organ. Within the penis is the external opening of the urethra, which is used for urination and ejaculation for urine and semen, respectively. Within the penis are erectile bodies, which engorge with blood during sexual (psychological or physical) stimulation, which result in an erection of the penis. This, in turn, results in an increase in the size and rigidity of the penis that can be used for sexual intercourse.
Penis is Made Up From the Glans, Body and Root
 The location of the penis is in the pubic region, just superior to the scrotum and inferior to the umbilicus, right at the body’s mid-line. Consisting of three regions, the penis is made up from the glans, body and root.
The location of the penis is in the pubic region, just superior to the scrotum and inferior to the umbilicus, right at the body’s mid-line. Consisting of three regions, the penis is made up from the glans, body and root.
- The glans: Also called the “Head” of the penis. This is the outer most segment of the penis, furthest from the body. The urethral opening exists here and hence where urine and semen can exit from the body. Consisting of erectile tissue, erections result in an increase in its size during sexual excitement.
- The body: Approximately cylindrical in shape, this is normally the largest portion of the penis. Responsible for a majority of the penis’s length, it is the most dynamic portion of the penis during sexual stimulation.
- The root: Responsible for connecting the penis to the rest of the body, it does so through the use of several thick ligaments such as the Suspensory Penile Ligament.
Tissue Layers and Types
 Consisting of several distinct tissue layers and types, the exterior of the penis is covered by flexible and elastic skin. Within the skin are high concentrations of stimulatory receptors responsible for the sense of touch and temperature.
Consisting of several distinct tissue layers and types, the exterior of the penis is covered by flexible and elastic skin. Within the skin are high concentrations of stimulatory receptors responsible for the sense of touch and temperature.
Deep to the penile skin are layers of tissue that contain blood vessels and connective tissue. Various kinds and layers of connective tissue, such as connective tissue known as tunica albuginea, help provide structure to the penis during erections. Deep to the tunica albuginea are the penile erectile bodies; the corpora cavernosa and the corpus spongiosum. These are the responsible for achieving and maintaining an erect penis. Once engorged with blood, they lengthen and thicken the flaccid penis.
Penis Functions
As a reproductive organ, one of it’s primary functions is for the delivery and deposition of semen into the vaginal canal, necessary for female egg fertilization. This is usually possible during the erect state so that the rigid penis can penetrate the female vagina. Another function of the penis is as an excretory organ which allows for delivery and excretion of urine from the body.
If you, or someone you know has more questions about the penis or it’s anatomy, consult your primary care doctor or urologist today!