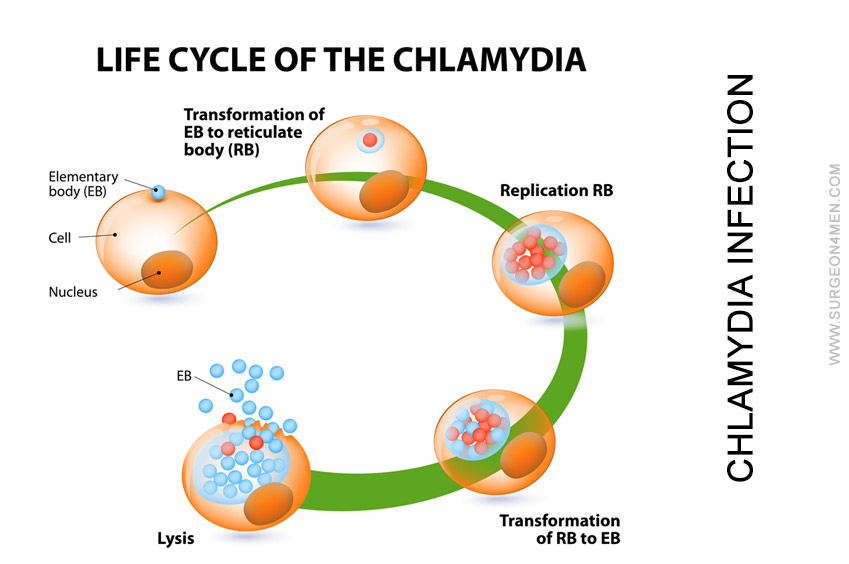
What Should we know about Chlamydia Infection?
Chlamydia infection is one of the commonest sexually transmitted infections in the US. It is caused by a bacterium known as Chlamydia trachomatis. The infection can easily be transmitted to unsuspecting sexual partners as it does not produce any symptom for a long time. According to statistics, 75% of women and 50% of men suffering from chlamydia infection do not show any symptom of the disease.
Symptoms of Chlamydia Infection
Although in most of the cases, the disease does not produce any symptom, the symptoms become visible in 2 to 3 weeks after sexual contact in few subjects. Some of the common symptoms of chlamydial infection are:
In women
 Vaginal discharge with an offensive odor
Vaginal discharge with an offensive odor- Bleeding in the middle of menstrual cycle
- Dysmenorrhea
- Pain in lower abdomen
- Low grade fever
- Burning and itching in the private parts
- Painful micturition
- Painful intercourse
In men
- Abnormal discharge from the tip of the urethra
- Painful micturition
- Burning and itching in private parts
- Testicles become swollen and painful
- Pain in lower abdomen
In certain patients, chlamydia infection may be present in the rectum. Such patients complain of pain, abnormal discharge and bleeding from the rectum. If the disease has been transmitted by way of oral sex, the patient may complain of pain in throat which becomes severe during swallowing, fever and cough.
Diagnosis of Chlamydia Infection
In few individuals who present with symptoms, the infection is diagnosed with the help of pathological examination. Swabs taken from the cervix or tip of urethra are sent for examination where the bacteria are identified. Urine examination may also be helpful at times. In some cases, swab from the throat or rectum may also show the presence of the bacteria.
Treatment of Chlamydia Infection
As the infection is caused by bacteria, it usually responds well to a course of antibiotics. Normally Azithromycin once a day or Doxycycline twice a day, are prescribed for a week. In case of severe infection, intravenous administration of antibiotics may be required. It is advised that even if one of the sexual partners exhibits symptoms of the infection, both of them should complete the antibiotic course. Otherwise, there is scope of repeated infection.
Complications of Chlamydia Infection
 If the disease is treated well in time, it resolves without causing any long term complications. However, if left untreated, chlamydia can cause severe complications in both men and women. In women, untreated chlamydial infection may result in pelvic inflammatory disease damaging the uterus, ovaries and the cervix. It may also damage the fallopian tubes leading to infertility. If a pregnant woman delivers vaginally before being treated, the new born baby runs the risk of developing eye infections and pneumonia.
If the disease is treated well in time, it resolves without causing any long term complications. However, if left untreated, chlamydia can cause severe complications in both men and women. In women, untreated chlamydial infection may result in pelvic inflammatory disease damaging the uterus, ovaries and the cervix. It may also damage the fallopian tubes leading to infertility. If a pregnant woman delivers vaginally before being treated, the new born baby runs the risk of developing eye infections and pneumonia.
In men, epididymis, the tube that carries the sperms from the testicles to the vas deferens, may get inflamed and become painful. Epididymitis may lead to infertility as well as severe low back pain in males.
Prevention of Chlamydia Infection
Like any other sexually transmitted disease, chlamydia infection can also be prevented by using barrier contraceptives. It is best to avoid multiple sexual partners and unnatural sexual practices. Before embarking on a new sexual relationship, it is advisable that both the partners should get tested for the presence of any sexually transmitted disease.
Reference: